ITR: For Income Tax purposes, an individual is classified as a Senior Citizen if they are at least 60 years old but not yet 80 years old at any point during the previous year. Furthermore, if an individual reaches the age of 80 years or more at any point during the previous financial year, the Income Tax Authority considers them a Super Senior Citizen.
Meanwhile, section 194P of the Income Tax Act, 1961 outlines the conditions under which Senior Citizens are exempt from filing their income tax returns. Additionally, this section is applicable from April 1, 2021.
Conditions For Exemption
- To qualify, the Senior Citizen must be 75 years of age or older.
- The Senior Citizen must have been a “Resident” of India for the entire previous year to qualify for the exemption.
- To qualify, the Senior Citizen’s income should only consist of pension income and interest income, with the interest income being earned from the same bank where they receive their pension.
- To avail of the exemption, the Senior Citizen must submit a declaration form to the designated bank.
- The specified bank, as designated by the Central Government, will be accountable for deducting Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) from the Senior Citizen’s income, taking into account deductions under Chapter VI-A and rebate under Section 87A.
- Upon the specified bank deducting taxes on behalf of senior citizens aged 75 and above, these individuals will be exempt from filing their income tax returns.
ALSO READ: RBI MPC Meeting: What Are The Key Takeaways On GDP, Interest Rates, And Economic Outlook?
ITR Details For Senior Citizens Otherwise
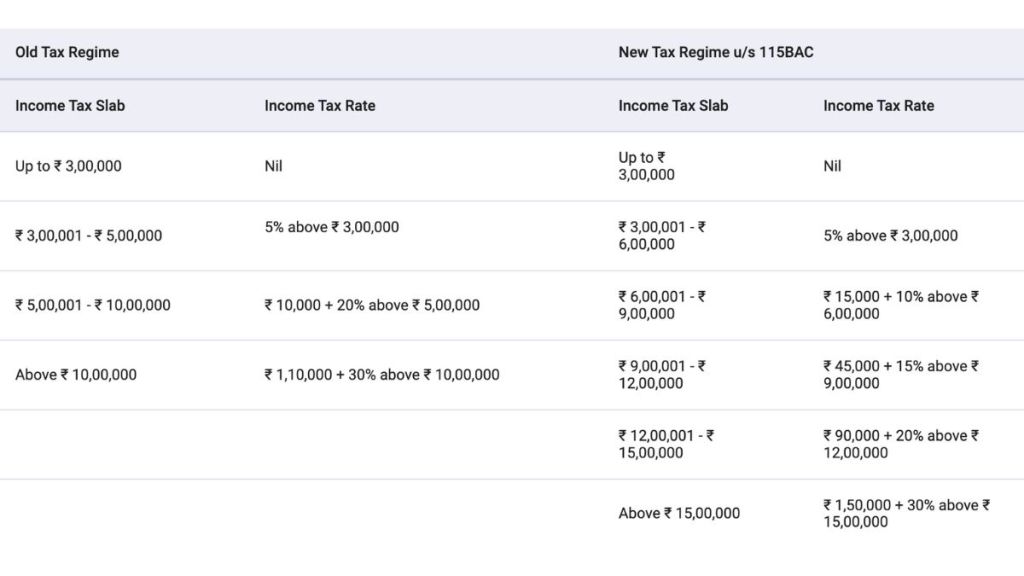
Tax Rates for Senior Citizens (60-79 years old):
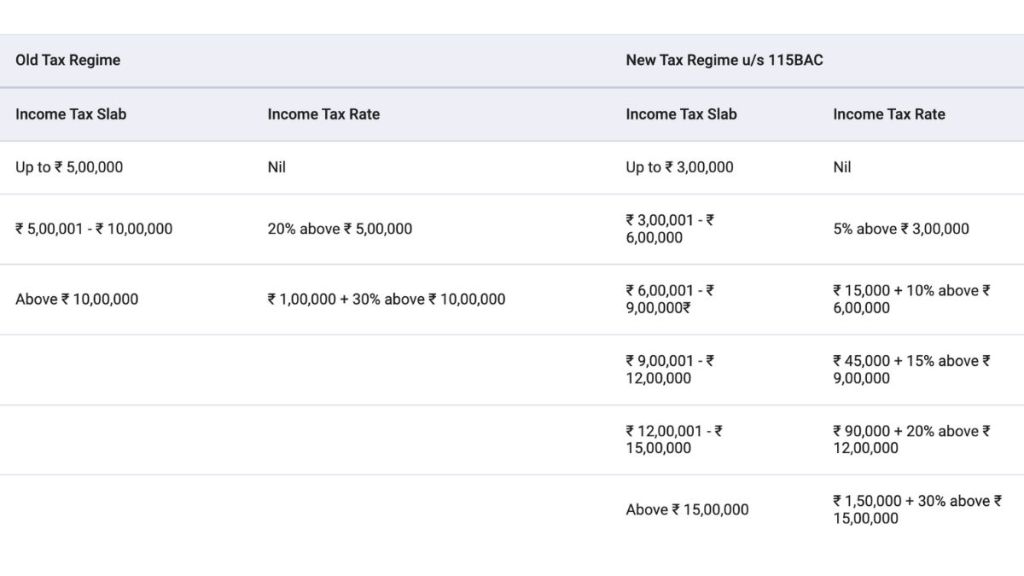
Tax Rates for Super Senior Citizens (80 years and above):
ALSO READ: 8th Pay Commission: Statements By Finance Ministry And NC-JCM – Will Salaries Rise By 186%?













