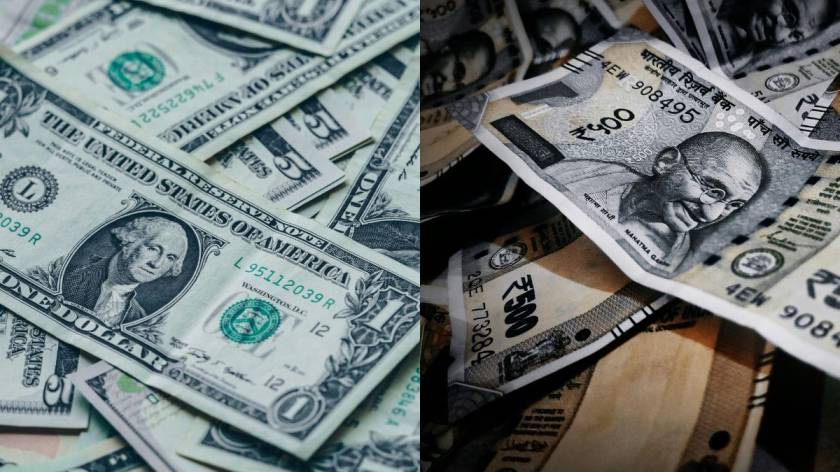
The Indian rupee (INR) downward spiral continued for the second consecutive day on Monday, plummeting 27 paise to reach an all-time low of ₹86.31 against the US dollar. The decline was fueled by the strength of the US currency, coupled with turbulent global market conditions.
The INR faced intense pressure due to several factors, including an unprecedented spike in crude oil prices, persistent foreign capital outflows, and a downturn in domestic stock markets. Meanwhile, a stronger-than-expected US jobs report boosted the dollar, while also driving up benchmark treasury yields, as investors now anticipate a more gradual pace of interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve.
Rupee Falling Against USD: Who Suffers The Most?
The depreciating INR has many consequences, affecting not only the government but also the public. When the INR falls, imports become costlier, while exports become more expensive. As a result, the government has to use more INR to import essential goods, such as oil and gold. Notably, India relies heavily on imported oil, meeting over 80% of its needs through foreign sources. Consequently, a weaker INR leads to higher retail prices for petrol and diesel, impacting the common man directly.
Moreover, Indians are the biggest losses if the INR falls, as they grapple with rising inflation. Furthermore, students aspiring to study abroad, particularly in the US, are severely affected, as they must pay tuition fees in dollars and the weakening INR means they have to spend more INRs to convert it in US Dollars, adding to their financial burden.
On the other hand, the US dollar’s strengthening against the INR is a blessing for the US and countries that export goods to India, as international trade heavily relies on US dollars. Additionally, Indians working in the US benefit from this exchange rate, as converting their dollars to INR translates into a higher value of Indian currency, increasing their purchasing power when in India.
ALSO READ: 8th Pay Commission: 186% Salary Hike For Central Govt Employees Soon – What All We Know?